How to Install Fallback Status Point in SCCM | ConfigMgr FSP
In this guide, I will show you how to install fallback status point in SCCM. You can use a ConfigMgr fallback status point to monitor client deployment for Windows computers.
After you set up fallback status point, you can identify the Windows computer clients that are unmanaged because they can’t communicate with a management point.
Note that you must assign an FSP to a client during the client installation. Therefore, plan to set up an FSP role before deploying clients. The fallback status point is an optional role in SCCM but recommended site system role that helps you manage clients and find any problems with clients.
What is Fallback Status Point?
A fallback status point (FSP) is used for monitoring client deployment for Windows computers in Configuration Manager and identifying unmanaged clients due to their inability to communicate with a management point. The ConfigMgr fallback status point role provides an alternate location for clients to send status messages during installation when they are unable to communicate with their management point.
When you set up a primary site for client management, the Fallback Status Point site system role is not installed. You have to manually install the FSP role on the dedicated site server. The installation of the FSP role is supported on child primary sites and standalone primary sites, but not on central administration sites or Secondary Sites.
The following client types don’t use a fallback status point in Configuration Manager:
- Mac computers and Mobile devices that are enrolled by Configuration Manager.
- Mobile devices that are managed by using the Exchange Server connector.
- A fallback status point isn’t required to monitor client activity and client health.
Security Risks associated with ConfigMgr Fallback Status Point
The fallback status point role always communicates with clients over HTTP, which uses unauthenticated connections and sends data in clear text. This makes the fallback status point easy to attack, especially when it is used with internet-based client management. Always set aside a server to run the fallback status point. This will help reduce the attack surface. Don’t install other site system roles on the same server in a production environment.
Any security risks connected with unauthenticated connections and clear text transfers via HTTP traffic are outweighed by the advantages of having a fallback status point. If the security dangers of operating a website with unauthenticated connections and clear text transfers outweigh the advantages of detecting client communication issues, don’t add a fallback status point.
When should you install ConfigMgr FSP Role?
Microsoft says that you must set up a fallback status point if all of the following are true:
- You want client communication errors from Windows computers to be sent to the site, even if these client computers can’t communicate with a management point.
- You want to use the Configuration Manager client deployment reports, which display the data that’s sent by the fallback status point.
- When you have a dedicated server for this site system role and have additional security measures to help protect the server from attack.
Fallback Status Point Prerequisites
Windows Server roles and features for the FSP: Depending upon the version of Windows Server, enable one of the following features:
- BITS Server Extensions and the automatically selected options
- Background Intelligent Transfer Services (BITS) and the automatically selected options
IIS configuration: The default IIS configuration is required with the following additions:
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
Steps to Install Fallback Status Point in SCCM
We’ll now go through the steps of fallback status point installation in SCCM.
- In the ConfigMgr console, navigate to Administration > Site Configuration > Servers and Site System Roles.
- Right-click your Site System and select Add Site System Roles.

On the General tab of the “Add Site System Roles Wizard,” the site server’s computer account is used to install the FSP role. If necessary, you can install the role using a different account. Click Next.

You can specify a proxy server for this site system server to use when it connects to the internet. If you don’t have proxy server in the setup, click Next.

On the System Role Selection tab, from the list of roles, select Fallback Status Point for installation. Click Next.
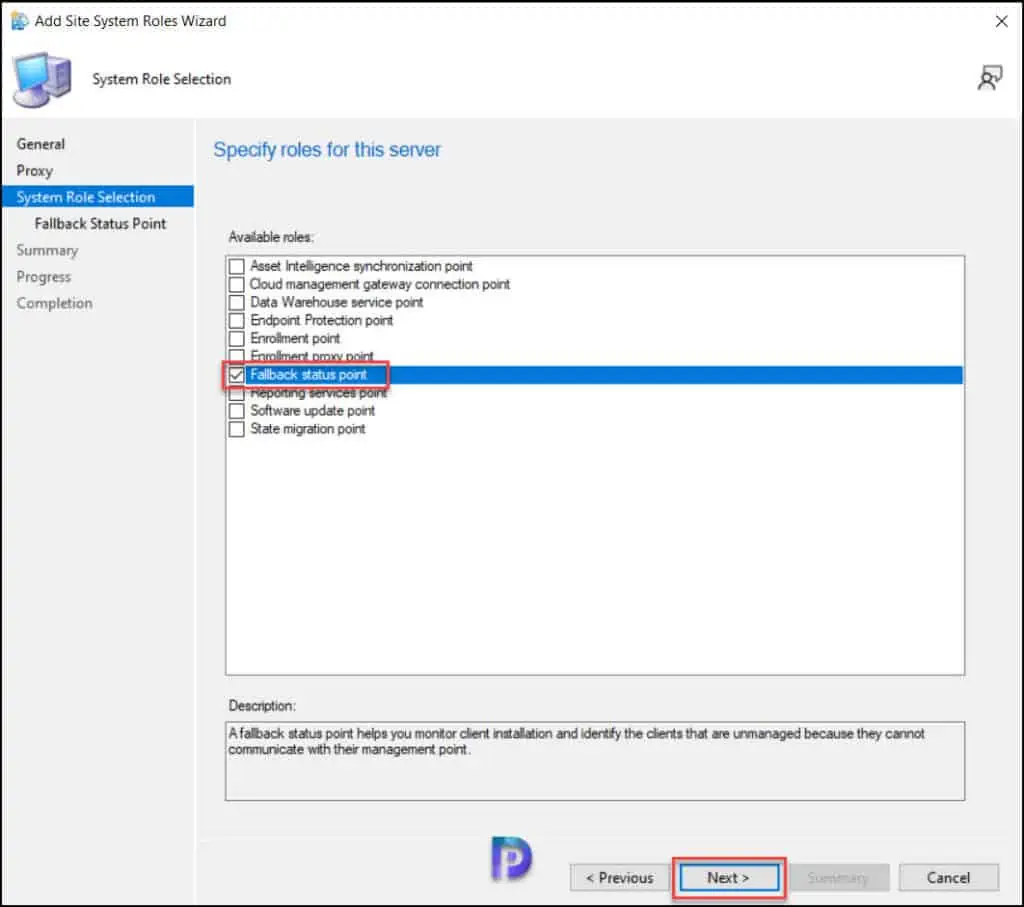
On the Fallback Status Point tab, specify the number of state messages to process. We recommend leaving the default value. To continue, click Next.

On the Summary tab, review the settings configured for fallback status point installation, click Next.

Click Close on the Completion tab. This completes the procedure to install the FSP in SCCM.

Fallback Status Point Logs in ConfigMgr
To verify & troubleshoot the installation of the Fallback Status Point, you can review the following FSP log files.
| Fallback Status Point Log File Name | Description | Fallback Status Point Log File Location |
| FspIsapi.log | Records details about communications to the fallback status point from mobile device legacy clients and client computers. | Site system server |
| fspMSI.log | Records messages generated by the installation of a fallback status point. | Site system server |
| fspmgr.log | Records activities of the fallback status point site system role. | Site system server |

The following lines from the fspMSI.log confirms the successful installation of fallback status point role in SCCM.
Product: ConfigMgr Fallback Status Point -- Installation operation completed successfully. Windows Installer installed the product. Product Name: ConfigMgr Fallback Status Point. Product Version: 5.00.9096.1000. Product Language: 1033. Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation. Installation success or error status: 0.
